You come across software every day. Whether you are sending emails, designing graphics, or running a business, software makes every task easier. With SaaS, now the software is just a few clicks away.
Wondering what is SaaS? You are in the right place. This blog breaks down its definition, explains how it works, outlines its business models, and explores how it is shaping the future of businesses in the digital world.
30-Second Summary
For everyday tasks, we use SaaS tools without realizing it. From video conferences to streaming music, SaaS is dominating every digital aspect of our lives.
So, what is SaaS, and why is it everywhere? The answer is in this blog. Discover the meaning of SaaS, what distinguishes it from traditional software, and what the future holds for this rapidly growing model.
What is SaaS: A Simple Explanation
SaaS stands for “Software as a Service.” It is a way of using software online instead of downloading it. You simply open the browser, log in to the website, and use the software.
SaaS is a cloud-based model, and customers pay for it to access it over the internet. It provides monthly or yearly subscriptions with benefits, such as multi-user accounts and pricing plans.
Think of it like this: using SaaS is like buying a cupcake instead of baking it. You do not need to:
- Buy ingredients (hardware)
- Learn the recipe (install software)
- Clean up any mess (fix technical issues)
You pay for it, and it is ready to use.
What is the “Cloud”?
Before moving forward, let’s learn what the cloud is. It is a network of servers that run the software, store your data, and handle all the updates. Cloud providers offer their services to end-users through the internet.
For instance, using Google Docs to work instead of installing Microsoft Word on your laptop. Or watching movies on Netflix instead of downloading them to your device.
All of your data is stored on these servers rather than on your personal device. The cloud is divided into three primary models, each serving a different level of convenience and control:
SaaS (Software as a Service): Ready-to-use applications easily accessed online, such as Google Docs and Shopify.
PaaS (Platform as a Service): Tools for developers to build applications without worrying about servers, such as Heroku and Google App Engine.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): Virtual access to IT infrastructure, including servers, storage, and network.
How does SaaS work?
To understand what is SaaS, it is important to know how it functions. SaaS tools operate on cloud-based models. SaaS vendors host applications and data on their servers or use third-party cloud servers. You can access the data by using the browser.
Technically, SaaS service providers use a multi-tenant structure. It means that a single software is used by multiple users. This approach manages resources and divides the management and infrastructure expenses across customers.
Moreover, SaaS vendors manage the platforms you use, operating systems, and middleware. All in all, SaaS provides a convenient way to access applications for users. It also simplifies software management without the complexities of traditional software.
SaaS vs Traditional Software
The world of software has evolved significantly in the last decades. From traditional software to the cloud, this transformation has changed how we use technology today.

This dramatic evolution gave rise to two models: SaaS and traditional software. Both have unique characteristics and considerations. This section highlights these differences to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current technical landscape.
Key Differences
The significant differences between these models are:
- Deployment and Access
SaaS solutions offer quick deployment as the software is hosted on a cloud server. The accessibility from a browser or a lightweight app makes SaaS a time-efficient model. You can tap into it from anywhere in the world.
On the contrary, traditional software needs to be installed on individual devices. It can be complex and requires more technical resources. Access to the software may seem restricted as it is confined to your device only.
- Cost Structure
SaaS operates on a subscription model, meaning clients must pay a recurring fee. The cost is predictable, helping you in budgeting. Moreover, the subscription or pay-as-you-go approach is adaptable. However, long-term subscriptions can accumulate, surpassing the one-time investment of traditional software.
On the other hand, traditional software requires a one-time upfront investment for purchasing a license and other hardware. This cost is substantial. But after buying the software, you use it indefinitely, which can be cost-effective in the long run. It also comes with an unanticipated cost of software maintenance and updates.
- Maintenance and Updates
SaaS service providers are responsible for maintenance tasks, such as fixing bugs, releasing new features, and making regular updates. It takes the load off the users to maintain the software. As a user, you get the updated and secure version of the software.
In contrast, traditional software comes with the responsibility of maintenance for users. You need to install updates, ensure compatibility with other devices, and troubleshoot issues. While it offers control, you need a higher level of technical expertise to handle traditional software.
- Customization
SaaS applications allow customizability, allowing users to tailor the software to their pre-defined parameters. Customization options include adjusting workflows, changing the appearance, and automating processes. However, the need for a consistent framework for all users limits the customization.
On the other hand, traditional software provides the freedom to customize it as it resides on a user’s device. The flexibility is ideal for businesses that have unique needs. However, significant customization also increases complexity and requires a high level of technical expertise to manage.
- Integration
SaaS platforms easily integrate with other cloud and web-based applications. They are accessible using APIs and other integration methods. It creates a seamless and cohesive workflow for businesses.
On the contrary, traditional software can be integrated with other systems. However, it may be complex and expensive, as you require additional programming and custom development.
- Security and Privacy
SaaS service providers generally manage data privacy and security. Users rely on the software provider’s commitment to safeguard their sensitive information. It is necessary to evaluate the credentials and certifications of a provider before making any commitments. Moreover, data breaches and unauthorized access are the main concerns.
In contrast, the user or organization is responsible for safeguarding data on traditional software. It is advantageous for businesses with specific security and compliance requirements. However, it also necessitates investing in different security infrastructures. You must install firewalls, antivirus software, and conduct regular security audits to ensure optimal security.
| Feature | SaaS | Traditional Software |
| Installation | Not required | Must install on each device |
| Access | Anywhere via the internet | Only on installed devices |
| Cost | Subscription (monthly or annually) | One-time investment or license |
| Updates | By provider | Manual updates |
| Data Storage | Cloud-based | Store locally |
The SaaS Business Model Explained
The SaaS (software as a service) industry has been one of the fastest-growing in the world. Understanding the SaaS model is essential when building a plan for your business’s growth.
How does the SaaS Business Model work?
Understanding what is SaaS and how its models impact businesses helps entrepreneurs create long-term growth strategies. Let’s see the pillars of the SaaS business model.
- Recurring Payments
As mentioned earlier, SaaS is a subscription-based model. Customers do not buy hardware; instead, they pay a monthly or annual fee. This recurring payment becomes the “monthly recurring revenue,” also known as MRR.
As SaaS companies provide services, not products, accounting for revenue can be challenging. When a customer signs your contract, you get some money upfront. But that does not equate to generating revenue until you earn it.
This money is a liability, and your customer can ask for it back if you do not deliver your service properly. Therefore, revenue recognition is a vital part of the SaaS business model.
- Customer Retention
Every business needs customer retention, but in SaaS, it is particularly important. Customer retention is the only thing that moves your business forward. You cannot say you earned money if your customer signs up for 12 months of service but leaves after 2 months.
It means that for the next 10 months, you will be without any revenue. This is why the SaaS model values cultivating customer relationships and upselling.
An old customer is likely to spend more than a new client. However, an existing client is 7 times more likely to leave your service and go to a competitor for a better product.
- Consistent Updates
SaaS platforms are frequently updated to keep the end-user happy. These smaller yet regular upgrades ensure a better customer lifetime value. Being in the software business puts customers’ information at risk of being breached and hacked.
Therefore, the SaaS business model prioritizes continuous assessment of the state of security fixes. As they host their own products, SaaS companies can come up with new features and enhanced versions of old ones.
This, combined with good customer communication, makes SaaS businesses highly responsive and user-centric.
Real-Life Examples of SaaS
You might be using SaaS applications without realizing that they are software-as-a-service. Let’s see some real-life examples of SaaS.
Google Workspace: Users subscribe to Google Workspace, while Google handles the maintenance and updates of this application.
Zoom: This platform provides video conferencing software accessible through a web browser and a dedicated app. Users have to pay for subscriptions to use its features.
Dropbox: It offers cloud-based file storage, synchronization, and sharing services over the internet. You do not have to install or maintain the software on your device.
Canva: This application operates on a freemium model. It means that while some features are free, you need to pay to unlock premium features.
Shopify: It is a subscription and cloud-based e-commerce platform. Businesses can manage their online stores without the need for software installation and maintenance.
Types of SaaS Products
To fully grasp the fundamentals of SaaS, you need to understand the various types of products.
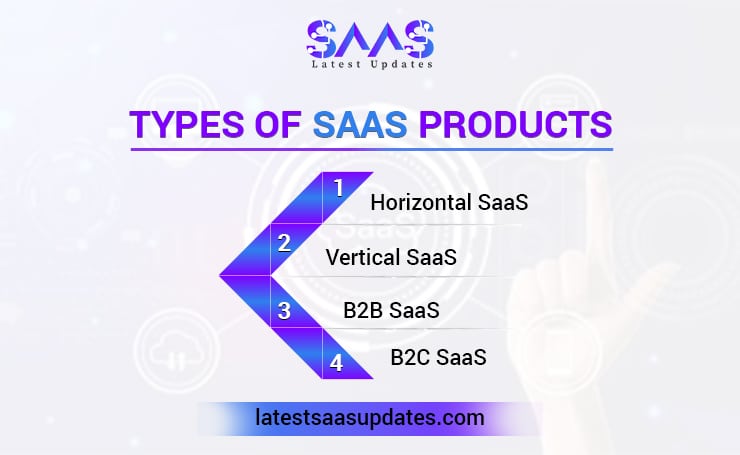
Horizontal SaaS
Horizontal is a type of SaaS products that target a wide audience of business users. In other words, Horizontal SaaS emphasizes satisfying business needs rather than catering to individual consumers.
This model has been used for almost a decade and is more mature than vertical SaaS. Horizontal SaaS companies focus on providing services to multiple industries. Some examples are:
- Salesforce (CRM)
- HubSpot (marketing)
- QuickBooks (accounting)
Vertical SaaS
The Vertical SaaS model targets a specific niche and focuses on target-specific standards. It is a recent phenomenon and is not as mature as the Horizontal SaaS. As it does not cover a broad product market, it narrows the industry’s scope.
Vertical SaaS takes a much narrower approach than Horizontal SaaS. It requires fewer resources as it is a small market with an emphasis on small industries.
- Guidewire (insurance)
- BiolQ (Med Tech)
- Health Assurance Plan (dental software)
B2B SaaS
B2B SaaS, or Business-to-Business Software as a Service, is built to cater to the needs of organizations, businesses, and enterprises. The B2B SaaS model has many advantages, including cost-effectiveness, improvements, regular updates, and scalability.
Moreover, you can access the software anytime and from anywhere in the world with an internet connection. The examples for B2B SaaS are:
- Slack
- SalesForce
- WorkDay
B2C SaaS
B2C SaaS stands for Business-to-Consumer Software as a Service. This model serves individual consumers with cloud-based applications. Users can access the software via a web browser, smartphone, or other devices.
The biggest advantage of B2C SaaS is that users do not have to install software on their devices. They pay as they go for the features they use on applications. Some famous examples of B2C SaaS are:
- Spotify
- Duolingo
- Grammarly
Pros and Cons of SaaS
The SaaS model has its fair share of advantages and disadvantages. Here is a breakdown of SaaS pros and cons.
Benefits of SaaS
- SaaS typically does not require a significant upfront cost. The provider takes care of maintenance, reducing hardware and other expenses.
- The applications are already installed and configured in the cloud. It reduces the delays that otherwise come with traditional software deployment.
- SaaS platforms are easily accessible. All you need is an internet connection and your device, and you can use the applications.
- SaaS providers usually offer scalability. The flexibility in options allows you to adjust your subscription plan without changing hardware.
Disadvantages of SaaS
- The control of the SaaS is with the provider. You use the latest version without the option to defer upgrades.
- Users may have concerns about security. Protecting sensitive information and managing access are major considerations around cloud-based applications.
- Despite becoming popular, SaaS has a limited range of applications. Many platforms still do not provide a hosted platform.
- You need to have a strong internet connection to access SaaS applications. An internet outage means losing access to your data.
- You may face slow performance of SaaS platforms as they are hosted online rather than on your local device.
Who Uses SaaS?
The flexibility of SaaS makes it popular in every industry. From individual consumers to large organizations, the SaaS model enhances convenience and productivity.
SaaS is used by:
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs): SaaS offers budget-friendly and scalable options for businesses with limited IT resources.
Large Enterprises: In larger organizations, SaaS provides robust solutions to complex problems, customer relations, and data analytics.
Specific Industries: SaaS offers industry-specific solutions and is tailored to various niches, such as healthcare, finance, education, e-commerce, retail, and manufacturing.
Freelancers: SaaS is excellent for freelancers who need cloud-based applications.
Remote Workers: SaaS enables remote workers to collaborate effectively by sharing files, managing projects, and conducting video conferences.
General Consumers: People use SaaS for entertainment (streaming music and videos), communication (messaging apps), and improved productivity (email and document platforms).
Why SaaS Is the Future of Software?
With the rapid evolution and integration of SaaS, it is the future of software. Organizations that understand what is SaaS easily adapt to the digital future.

According to Fortune Business Insights, the SaaS industry will grow from USD 315.68 billion in 2025 to USD 1,131.52 billion by 2032. Moreover, SaaS will power 85% of business applications by 2025.
The trends revolutionizing the future of saas are:
- AI is taking the ground in SaaS and modifying it for the better. AI-powered SaaS can streamline your workflow and reduce manual tasks.
- SaaS enables the rapid deployment of new software solutions for businesses, allowing them to address market changes quickly.
- SaaS providers continuously improve their applications. Businesses can stay ahead of the technological curve and provide a better customer experience.
- The data is stored in multiple locations. In any disaster or outage, it ensures business continuity.
- With robust API platforms, the integration of different technological tools creates a digital ecosystem, making SaaS indispensable.
Final Thoughts
SaaS is no longer a trend; it is making its mark on the world of technology. As businesses are embracing digital transformation, this model is becoming increasingly dominant.
In this blog, we covered what is saas and how it works. We explored its benefits, types of SaaS products, and its influence in the digital landscape. For more updates on SaaS and its impact, feel free to visit the Latest SaaS Updates.
FAQs
What does SaaS stand for?
SaaS stands for Software as a Service. It is a way of delivering software over the internet without the need for downloading it to your device.
Is Zoom a SaaS Application?
Yes, Zoom is a SaaS platform. It delivers video conferencing and communication services through the internet. It follows a subscription model, allowing you to access it remotely.
Why SaaS is the best Business Model?
SaaS is considered an ideal business model because of its convenience, scalability, and cost-effectiveness for businesses and consumers. Through SaaS, your business faces a lower entry barrier, predictable revenue, and high customer retention.

